An Increase in Temperature Affects the Reaction Rate by
Also KE where k boltzmann constant T temperature. The concentration and volume of both sodium thiosulphate solution and sulphuric acid are kept constant in each set of the experiment.
Section 13 3 The Rate Of A Reaction
The effect of increasing collision frequency on.
. This can be answered by Arrhenius equation. An increase in temperature increases the rate constant and hence the rate. Even where it is approximately true it may be that the rate doubles every 9C or 11C or whatever.
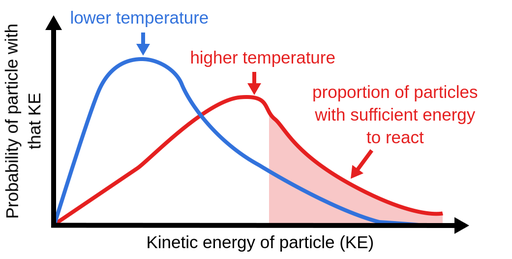
In order to illustrate the dominance of the effect of temperature change on the reaction rate consider a reaction in which the temperature of the system is raised from 310C to 400C. The reaction rate decreases. When temperature increases the amount of atomic or molecular collisions between molecules increases.
You mustnt take this too literally. The reaction rate increases. K A e E a R T.
T Temperature in absolute scale in kelvins. The fact that the rate increases does not imply the rate constant changes. The rate of reaction will probably have doubled for that increase in temperature - in other words an increase of about 100.
Where k rate constant of the reaction. So kinetic energy is proportional to temperature. Adecreasing the velocities of particles that collide in the reaction.
Hence when temperature will increase the kinetic energy will also increase. From the data in table II the reaction rate increases from 03645 to 07335 when the temperature is increased from 20C to 30C. A catalyst changes the rate of reaction but is.
The number of degrees needed to double the rate will. Hence there will be increase in rate of reaction. As a result collision between the molecules will increase.
Effect of Temperature on Enzymatic Reaction. An increase in temperature affects the reaction rate by. As a rough and ready guide increasing the temperature by 10C doubles the rate of a reaction.
Thats an increase of 17 for a 10 rise. But the change in reaction rate with temperature is not just a function of the temperature. If you increase the temperature from 293 K to 303 K 20C to 30C you will increase the collision frequency by a factor of.
Absolute temperatue From the equation. A ten degree centigrade rise in temperature will increase the activity of most enzymes by 50 to 100. Instead temperature increases actually affect the rate constants written k of reactions in a predictable way.
The effect of temperature on reaction rates Athe collision theory. Pre-exponential constant correlating with the valid collision in the reaction Ea. Frequency of collisions and energy of collisions.
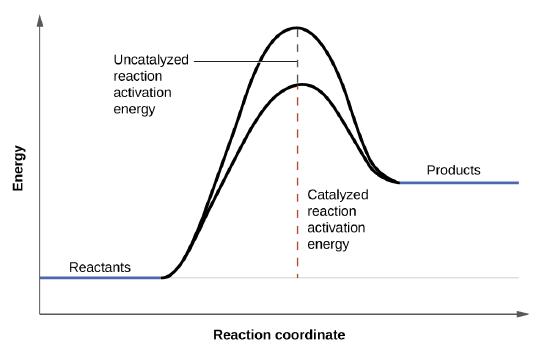
A catalyst increases the speed of a reaction by changing the reaction mechanism. The rate of the catalyzed reaction will be greater. We can identify five factors that affect the rates of chemical reactions.
However increasing the rate does not increase the rate constant. In other words as the temperature increases the rate of reaction also increases. C2H4g H2g mc030-1jpg C2H6g.
Chemical reaction rates increase or decrease according to factors including temperature pressure and light. Variations in reaction temperature as small as 1 or 2 degrees may introduce changes of 10 to 20 in the results. A sure in temperature increased kinematic energy that led to faster movement and collision of particles thus leading to a rise in the rate of reaction.
Answer 1 of 7. The reaction rate does not change. Any change in rate of reaction is due.
In general terms an increase in temperature increases the rate of. The new mechanism will provide steps with lower activation energies. Universal gas constant T.
Ea Activation Energy for the reaction in Joules mol 1 R Universal Gas Constant. Usually the rate of a reaction approximately doubles for every 10C rise in temperature. The increase in energy is usually the more important factor.
It is implied that increasing the rate constant will increase the rate of reaction. Here is the Arrhenius Equation on the temperature dependence of the rate of a chemical reaction. As temperature increases so do the rate of enzyme reactions.
How does an increase in the reactant concentration affect the reaction rate of a chemical reaction. The effect of temperature on the rate of reaction is due to two factors. The chemical nature of the reacting substances the state of subdivision one large lump versus many small particles of the reactants the temperature of the reactants the concentration of the reactants.
It doesnt apply to all reactions. Because more molecules will have the lower activation energies required for the catalyzed reaction more molecules will react during a unit of time. The rates at which reactants are consumed and products are formed during chemical reactions vary greatly.
Likewise whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic activation energy is required to initiate the reaction which is essentially obtained by increasing the temperature of the reactor to an optimum point where the particles are ready to collide and initiate the reaction. Bincreasing the number of molecules that have sufficient kinetic energy to react. KAe-EaRT In the equation k.
Consider the reaction below. A Arrhenius Constant. How does an increase in the temperature of a chemical reaction affect the reaction rate.
Now if the temperature coefficient for 10C temperature-rise is 2 the relative increase in the rate constant or rate will be 2 1 2 1 2 400310 10 3.
Factors That Affect Reaction Rates Labster Theory

Effect Of Temperature On Rate Of Reaction Arrhenius Equation With Faq S

8 3 Factors Affecting Reaction Rates Kinetics Chemistry Libretexts
Factors That Affect The Rate Of Reactions Introductory Chemistry
Comments
Post a Comment